Does Insulated Vinyl Siding Reduce Noise?

As the inventors of insulated vinyl siding, we have received hundreds of testimonials from customers over the years claiming that insulated vinyl siding made their homes quieter than before the siding was installed. Whether the noise was a neighbor’s barking dog, street traffic sounds, or a heavy thunderstorm, wrapping the home in a layer of insulation seemed to dampen noises from the outside. Despite many of these claims, it has been difficult to answer the question "Does insulated vinyl siding reduce noise?", until now. We commissioned a third-party test laboratory to conduct a sound transmission loss test to determine how much insulated vinyl siding products truly reduce noise on exterior wall assemblies.
At a high level, the results obtained through testing confirmed that insulated vinyl siding can reduce noise by up to 39% compared to the base wall tested. This confirmed homeowner claims that having insulated vinyl siding installed made their homes quieter than before. In addition, testing showed that insulated vinyl siding reduces sound transmission 8x more than fiber cement.
About Sound
The range of sounds a human being can hear depends on both the pitch and loudness of the sound. Pitch, whether it is high or low, is measured in Hertz (Hz), and loudness is measured in decibels (dB).
For a person with normal hearing, the human hearing range for pitch starts as low as 20 Hz, while the highest possible frequency heard without discomfort is 20,000 Hz. Our hearing is most sensitive in the 2000-5000 Hz frequency range.
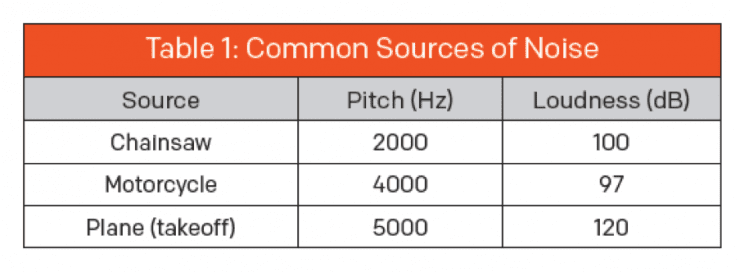
In terms of loudness of sound, humans can typically hear 0 dB, while sounds that are more than 85 dB can be dangerous in the case of prolonged exposure. Table 1 shows some common sources of noise and their pitch in Hertz, as well as their loudness in decibels.
About the Sound Transmission Test
Sound transmission loss as defined ASTM C634 refers to “the response of specimens exposed to a diffuse incident sound field, and this is the test method condition approached by this laboratory test method. The test results are therefore most directly relevant to the performance of similar specimens exposed to similar sound fields. They provide a useful measure of performance for the variety of sound field sto which a partition or element may typically be exposed.
A wall assembly specimen was constructed in the laboratory. Sound transmission loss test was initially performed on a filler wall. The 96” wide by 96” high specimen plug was removed from the filler wall assembly. The specimen was then placed on an isolation pad in the test opening.
Duct seal was used to seal the perimeter of the specimen to test the opening on both sides. The interior side of the specimen, when installed, was approximately 1/4” from being flush with the receive room side of the filler wall. A stethoscope was used to check for any abnormal air leaks around the test specimen prior to testing.
Procedure
The sensitivity of the microphones was checked before measurements were conducted. The transmission loss values were obtained for a single direction of measurement.
Two background noise sound pressure levels and five sound absorption measurements were conducted at each of the five microphone positions.
Two sound pressure level measurements were made simultaneously in receive and source rooms at each of five microphone positions.
The air temperature and relative humidity conditions were monitored and recorded during all measurements.
Test Methods and Standards
Results obtained are tested values and were secured using the designated test method(s):
- ASTM E90-09 (2016) Standard test Method for Laboratory Measurement of Airborne Sound Transmission Loss of Building Partitions and Elements
- ASTM E413-16 Classification for Rating Sound Insulation
- ASTM E1332-16 Standard Classification for Rating Outdoor-Indoor Sound Attenuation
- ASTM E2235-04 (2012) Standard Test Method for Determination of Decay Rates for Use in Sound Insulation Test Methods
Summary of Results
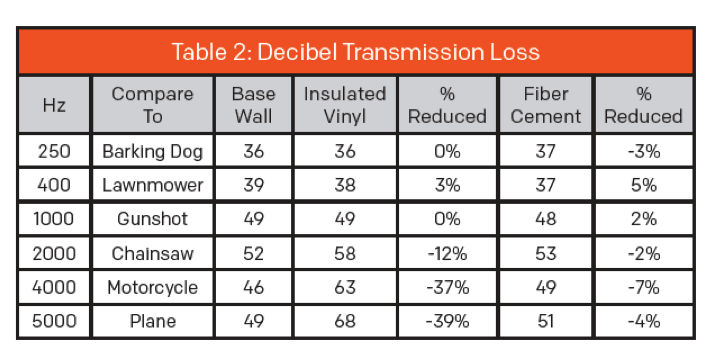
#1: INSULATED VINYL SIDING REDUCES SOUND TRANSMISSION BY UP TO 39%
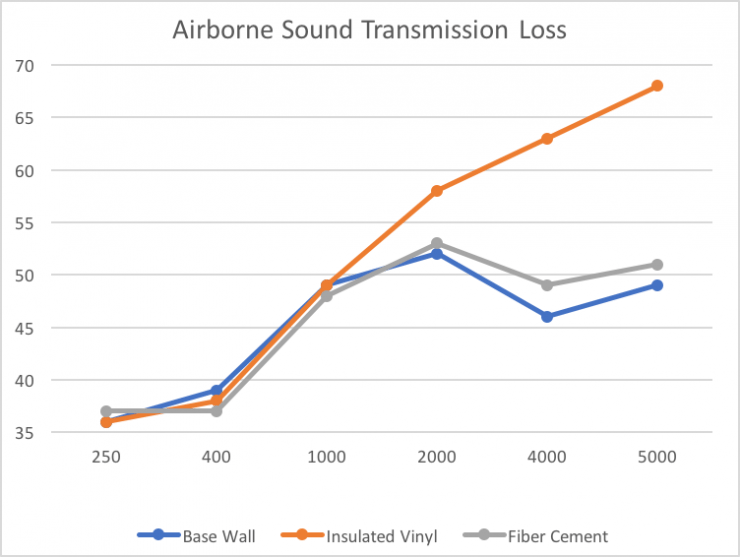
As the frequency rises, so does the amount of sound transmission loss. Insulated vinyl siding reduces noise best in the 2,000-5,000 Hz range, the humans most sensitive hearing frequency range.
#2 INSULATED VINYL SIDING REDUCES SOUND TRANSMISSION 8X MORE THAN FIBER CEMENT
As evidenced in Table 2, insulated vinyl siding reduces the sound transmission of 5000 Hz (comparable to a plane taking off) by up to 39%, while fiber cement reduces the sound by only 4%. This percentage of transmission loss is over 8x higher for insulated vinyl siding than fiber cement.
About Insulated Siding
Insulated vinyl siding is made of a contoured, rigid foam backer permanently adhered to vinyl siding. This provides a long lasting appearance, energy savings, and significantly improves impact resistance compared to traditional vinyl siding.
For more information, check out our article What Is Insulated Siding? Materials, Pros, Cons, and Installation >
Other Related Topics